Raynaud's disease, also known as Raynaud's phenomenon, is characterized by episodes of reduced blood flow to the extremities, including the fingers and toes, in response to cold temperatures or emotional stress. When Raynaud's affects the feet specifically, it can lead to discomfort and potential complications.
Read more
Spinal Structures
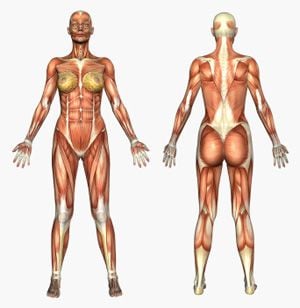 The spinal column is an intricate framework of interlocking bones that, when viewed from the side, form a gentle "S" shape. The spine is a sophisticated system— both fragile and sturdy— of muscles, bones, joints, ligaments, discs, a spinal cord, and nerves.
The spinal column is an intricate framework of interlocking bones that, when viewed from the side, form a gentle "S" shape. The spine is a sophisticated system— both fragile and sturdy— of muscles, bones, joints, ligaments, discs, a spinal cord, and nerves.
Joints, called "facet joints," and discs allow the spine to bend and twist and absorb mild shocks and bumps. The brain, spinal cord, and nerves manage your body's movement by sending messages to muscles. Supporting the entire structure is an intricate system of ligaments, tendons, and discs.
The vertebrae, facet joints, and discs are vertically stacked in a healthy spine. Ligaments support that alignment and discs, which are flexible, spongy pads, absorb shocks between the vertebrae and joints.
The spine has four natural curves, which help to evenly distribute the loads incurred by daily activity—from sitting, walking, and running, to lifting and carrying.
There are three major parts of your spine:
- The cervical spine, or neck
- The thoracic spine, or upper back
- The lumbar spine, or lower back
The sacrum, which lies at the base of your spine between the fifth lumbar and the tailbone, or coccyx, is a triangular-shaped bone made up of five fused parts. These are called "S1, S2, S3, S4 and S5." These unique parts connect to your pelvis by way of structures called sacroiliac joints.
Your neck, which is also called the upper cervical spine, is distinguished by two large vertebrae. One is called the upper bone, or atlas, and the other is called the lower bone, or axis.
These bones in your cervical spine do not need discs and protect the medulla oblongata, or lower brainstem. Inside the medulla oblongata are reflex centers that regulate such things as your heartbeat, breathing, the diameter of your blood vessels, swallowing, vomiting, coughing, sneezing, and hiccupping.
Almost half your brain's 12 cranial nerves originate in the medulla and control such things as balance and hearing, taste, swallowing, salivation, the digestive system, head and neck muscles, and the tongue. One can easily see that if the upper bones of your spinal cord are out of alignment, a whole host of things can go wrong in your body, some subtle, some not-so-subtle. However, it is not uncommon for many of us to have some sort of misalignment in these structures as we go through the daily trials and tribulations of life.
Basically, your spine is composed of four types of material. These are:
- Vertebral bodies – These are the large bony structures you see in the spinal anatomy and essentially are the support column of your back. This amazing structure supports about half of your body's weight; your muscles do the job of the remaining half. Vertebral bodies are separated by small spaces containing discs. Most of the vertebral bodies in your spine have several joints that allow your back to bend and flex. When you bend forward, your hips provide about half of the impact, while your lower spine, or lumbar, takes on the rest.
- Vertebral discs – The shock absorbers that are found between vertebral bodies, discs are essentially made up of two major parts: a tough outer core and a soft inner core. When you are born, these discs are mostly water. As you get older, the discs slowly lose their water content and get harder. As they dehydrate over time, your discs provide less of that soft and cushy support they provided when they were new. Because they have no blood supply and few nerve endings, discs are unable to repair themselves. Disc degeneration can be painful in later years; in some cases, the inner core of the discs leak proteins that can inflame the nerve roots.
- Spinal cord and nerve roots – As it leaves the base of your brain, your spinal cord weaves through the neck and upper back, ending up at the bottom of your thoracic spine. Actually, your spine ends before it reaches your lower back, shooting off a series of nerve roots that are dispersed through bony canals throughout your body.
- Muscles – The soft tissue surrounding your spine is largely composed of muscles, which support your spine as it bends and flexes. Two large muscles in your lower back, called erector spinae, help hold up the spine.
Muscular System
The soft tissues that envelop and support your spine make up an intricate network of muscles.
With the help of your body's abdominal muscles, this network helps to keep your body stabilized and upright, and allows it to bend and flex.
The types of muscles that support your spine include:
- Extensors – These are composed of back and gluteal muscles. These muscles help keep your back straight, assist in efforts involving lifting, and moving your thigh away from the body.
- Flexors – These are your abdominal and iliopsoas muscles, which support the spine from the front. They also control the arch of your lower back and move the thigh in toward the body.
- Obliques (also called rotators) – These "side" muscles stabilize your spine when you are standing upright and help rotate your spine and maintain proper posture and spinal curvature.
Nervous System
Your nervous system looks much like an upended tree, suspended from its roots at the base of your brain, its millions of limbs reaching out to every corner of your body.
Your spinal cord is like a thick braid formed by billions of these nerves. Your body has approximately 15 billion nerve cells—all of which receive and transmit nerve impulses by way of the spinal cord. These impulses control virtually all functions of your body—from your senses to mobility.
Nerve roots and your spinal cord
Your spinal cord actually ends near the base of your upper back, shooting out braids of nerves called "nerve roots." These nerve roots run through a large tunnel-like canal, and at each level of your spinal column, a pair of nerve roots exits from the spine.
Nerve roots are named for the level of your spine they exit from, beginning with a letter and followed by a number. For example, a nerve root in the cervical spine may be called "C6,"while a nerve root in the lumbar region may be called "L4."
Innate intelligence, the knowledge we are born with, guides cells and organs to receive and transmit impulses to our brain through this vast network of nerves.
A healthy spinal cord allows these impulses to flow freely back and forth. But when your spinal cord becomes misaligned, its parts get out of place and nerves can become pinched. When this happens, the flow of information from your nervous system gets interrupted. This imbalance, called subluxation, can lead to physical and emotional problems ranging from minor discomfort to major illnesses.
-
Raynaud's Disease
Category: Ball/Joint/Tendon
-
Ridge Augmentation
Category: Treatment, Cosmetic Dentistry
If you lose one or more permanent teeth, an indentation may result in the gums and jawbone where the tooth used to be. When no longer holding a tooth in place, the jawbone recedes and the resulting indentation looks unnatural. Ridge augmentation is a procedure that can recapture the natural contour of
Read more -
Root Canal Therapy
Category: Treatment
Root canals are tiny passageways that branch off from beneath the top of the tooth, coursing their way vertically downward, until they reach the tip of the root. All teeth have between one and four root canals. Many tooth problems involve infections that spread to the pulp, which is the inner chamber
Read more -
Scaling and Root Planing
Category: Treatment
Some cases of acute periodontal (gum) disease that do not respond to more conventional treatment and self-care such as flossing may require a special kind of cleaning called scaling and root planing. The procedure begins with administration of a local anesthetic to reduce any discomfort. Then, a small
Read more -
Sealants
Category: Tooth Care
Sealants are liquid coatings that harden on the chewing surfaces of teeth and are showing a great deal of effectiveness in preventing cavities—even on teeth where decay has begun. The pits and grooves of your teeth are prime areas for opportunistic decay. Even regular brushing sometimes misses these
Read more -
Sealants
Category: Treatment
The pits and grooves of your teeth are prime areas for opportunistic decay. Even regular brushing sometimes misses some of these intricate structures on the chewing surfaces of your teeth. Enter sealants, which are thin coatings applied to the chewing surfaces designed to prevent the intrusion of
Read more -
Seniors and Oral Health
Category: Tooth Care
More and more people are avoiding the need for dentures as they grow older, going against the notion that false teeth are a normal part of growing older. In fact, there's usually no reason for you NOT to keep your teeth your entire life, providing you maintain a healthy balanced diet and practice
Read more -
Sensitive Teeth
Category: Dental Problems
If you wince with pain after sipping a hot cup of coffee or chewing a piece of ice, chances are that you suffer from "dentin hypersensitivity," or more commonly, sensitive teeth. Hot and cold temperature changes cause your teeth to expand and contract. Over time, your teeth can develop microscopic
Read more -
Sleep and Pain
Category: Lifestyle and Management
The Connection Between Sleep and Pain Sleep plays a vital role in our overall health and well-being, including pain management. Poor sleep can exacerbate chronic pain conditions, while good sleep can help alleviate them. Understanding this connection can help individuals manage their pain more effectively. The
Read more -
Smoking and Pain
Category: Lifestyle and Management
Smoking is a widespread habit that has significant implications for individuals’ health and lifestyle. One of the less discussed but equally important aspects is its relationship with pain. The Connection Between Smoking and Pain Research has shown that smoking can exacerbate pain. Nicotine, the addictive
Read more -
Speech Audiometry
Category: Diagnostic Audiology
Speech audiometry is a crucial component in audiology, offering a nuanced understanding of an individual's ability to perceive and comprehend spoken language. In this exploration, we delve into the intricacies of speech audiometry, uncovering its significance, methodologies, and applications in assessing
Read more -
Sports Injuries
Category: Fitness and Your Feet
Knee, foot, and ankle injuries are common occurrences among athletes participating in various sports and activities. These injuries can range from minor strains and sprains to more serious ligament tears and fractures. Understanding the specific types of injuries that affect the knee, foot, and ankle,
Read more -
Subungal Exostosis Bone Spur Under Toenail
Category: Nails & Skin
Subungual exostosis, also known as a bone spur under the toenail, is a condition characterized by the development of a bony growth beneath the toenail. This article explores the causes, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment options, and prevention strategies for subungual exostosis to provide individuals with
Read more -
Teeth Grinding (Bruxism)
Category: Dental Problems
Teeth grinding, also called bruxism, is often viewed as a harmless, though annoying, habit. Some people develop bruxism from an inability to deal with stress or anxiety. However, teeth grinding can literally transform your bite relationship and worse, severely damage your teeth and jaws over long
Read more -
Teeth Whitening
Category: Treatment, Cosmetic Dentistry
Whitening procedures have effectively restored the smile of people with stained, dull, or discolored teeth. The darker tissue of your teeth, the dentin, can become exposed as the outer layer of enamel is worn away by the effects of aging or things like caffeine and tobacco. Food particles are naturally
Read more -
Temporomandibular Joint (TMJ) Disorders
Category: Specialized Pain Conditions
Temporomandibular Joint (TMJ) disorders are a group of conditions that cause pain and dysfunction in the jaw joint and the muscles controlling jaw movement. The TMJ is one of the most complex joints in the body, allowing for a wide range of motion including opening and closing the mouth, chewing, speaking,
Read more
Contact Us
Send Us An Email
Our Location
Find us on the map
Hours of Operation
Our Regular Schedule
Monday:
8:00 am-5:00 pm
Tuesday:
8:00 am-5:00 pm
Wednesday:
8:00 am-5:00 pm
Thursday:
8:00 am-5:00 pm
Friday:
Closed
Saturday:
Closed
Sunday:
Closed